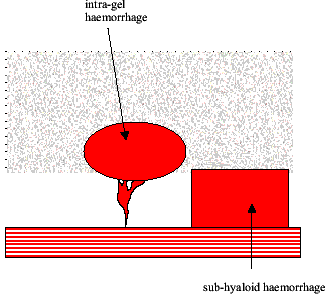
This bleeding occurs either between the retina and the vitreous gel (pre-retinal or sub-hyaloid haemorrhage) or into the middle of the vitreous gel itself (intra-gel vitreous haemorrhage).
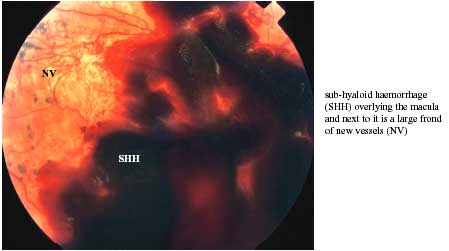
Pre-retinal or sub-hyaloid haemorrhage can only occur if the vitreous is still attached to the retina and “holding the blood up against it”.
If the vitreous detaches, as it often does, then the blood falls into the vitreous cavity converting itself into a vitreous haemorrhage. These vitreous haemorrhages often clear as the vitreous detaches (posterior vitreous detachment) further and falls inferiorly (downwards). If this does not occur then the blood must be surgically removed (vitrectomy).
NEW VESSEL SCARRING
New vessels always grow on a platform of glial (scar) cells. If the new vessel component predominates then vitreous haemorrhage occurs. Sometimes the glial part seems to predominate. This often happens if there has been repeated vitreous haemorrhage. Glial cells associated with new vessels growing along the major vascular arcades are particularly at risk. This is because the vitreous attachment is normally greatest along these arcades. The reaction between the glial cells and the vitreous results in scar formation. These scars contract and the vitreous appears to pull on the retina causing retinal folds and eventually the retina to detach.
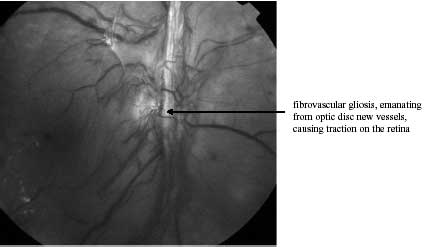
This form of retinal detachment is called a traction retinal detachment. It is concave in shape. It usually progresses very slowly unless a hole also forms in the detached retina. In this situation the retinal detachment converts to a convex rhegmatogenous (hole in the retina) retinal detachment. The hole in the retina allows fluid from the vitreous cavity to get under the retina lifting it off. Rhegmatogenous detachments progress rapidly and need to be surgically treated urgently.
